Understanding Nutrition Basics
Nutrition is a fundamental aspect of health and well-being, serving as the foundation for a balanced diet. At its core, nutrition involves the study of how food affects the body and its functions. This encompasses two main categories of nutrients: macronutrients and micronutrients. Each plays a critical role in supporting bodily processes and maintaining health.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!Macronutrients include carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Carbohydrates are the body’s primary energy source, fueling daily activities and functions. They can be found in foods such as grains, fruits, and vegetables. Proteins are vital for growth, tissue repair, and the production of enzymes and hormones. Sources of protein include meat, dairy, legumes, and nuts. Fats, while often misunderstood, are essential for nutrient absorption, hormone production, and providing a concentrated energy source. Incorporating healthy fats from sources such as avocados, olive oil, and fatty fish is crucial for a balanced diet.
Micronutrients, comprising vitamins and minerals, are required in smaller amounts but are equally important. Vitamins support various bodily functions including immune response and energy metabolism, while minerals contribute to bone health, fluid balance, and muscle function. A diet rich in a variety of fruits and vegetables ensures an adequate intake of these vital nutrients.
Additionally, dietary fiber plays an important role in digestion, helping to maintain gut health and prevent constipation. Foods high in fiber, such as whole grains, beans, and vegetables, contribute to prolonged satiety and can aid in weight management. Adequate hydration is also vital, as water supports numerous physiological processes, including temperature regulation and nutrient transport.
In understanding the basics of nutrition, one can appreciate the interconnectedness of these nutrients and how they collectively influence overall health and energy levels. A balanced diet comprising a variety of macronutrients and micronutrients supports growth, repair, and the body’s intricate systems.
Building a Balanced Diet

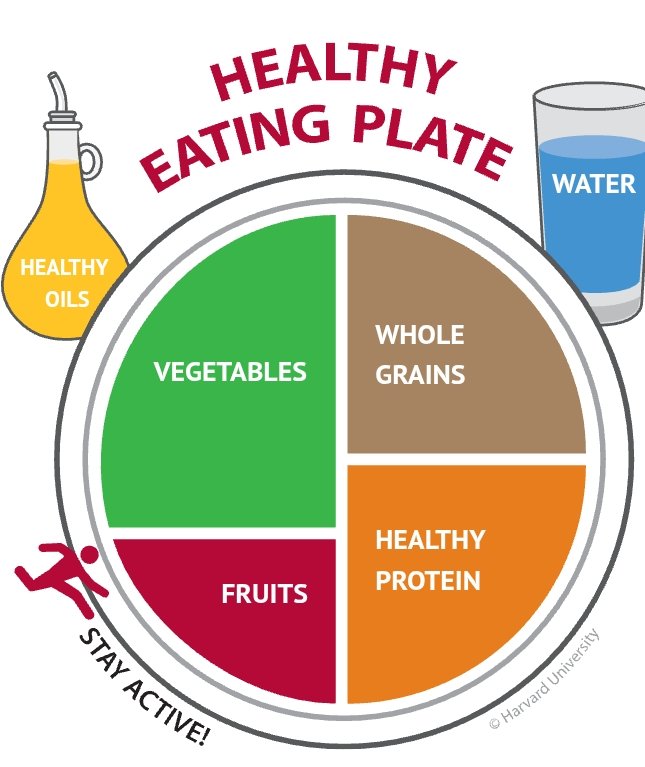
A balanced diet is foundational to achieving and maintaining optimal health. It involves incorporating a variety of food groups in appropriate proportions to provide the necessary nutrients for the body. A well-structured diet should include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. These components work synergistically to support overall wellness, enhance energy levels, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
Fruits and vegetables should constitute a significant portion of daily intake, ideally making up half of the plate at each meal. They are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that contribute to improved immune function and overall health. Aim for a colorful array of options, varying your choices to maximize nutrient diversity. Whole grains, such as brown rice, quinoa, and whole grain breads, should also be prioritized over refined grains. These carbohydrates provide essential fiber, which promotes digestive health and aids in maintaining a healthy weight.
In terms of protein, lean sources such as chicken, fish, legumes, and tofu are recommended. They are important for tissue repair and muscle maintenance. Incorporating healthy fats, like those found in avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, will help in nutrient absorption and provide energy. While these fats are beneficial, portion control is essential to avoid excess calorie intake.
Meal planning can be an effective strategy to ensure a balanced diet. Set aside time each week to plan meals based on seasonal produce and timely options. When shopping for ingredients, focus on the perimeter of the grocery store, where fresh foods are typically found. Additionally, when dining out, consider healthier menu options and practice portion moderation by sharing meals or requesting smaller servings.
Mindful eating is another important facet of a balanced diet. This practice encourages individuals to pay attention to their hunger cues and the sensory experience of eating, which can lead to improved digestion and satisfaction after meals. By adopting these strategies, one can cultivate a nutritionally sound diet that promotes overall health.
Incorporating Healthy Habits into Your Lifestyle

Adopting a healthy diet is a journey that necessitates practical strategies to integrate into daily life. One of the most effective methods is to set realistic goals tailored to individual lifestyles. Instead of enforcing drastic changes overnight, consider gradual adjustments that promote sustainable habits. For instance, start by incorporating one more serving of vegetables into your meals daily, gradually increasing as you become comfortable with these changes.
Understanding food labels is another essential aspect of maintaining a healthy diet. Familiarizing yourself with components such as serving size, calories, and nutritional values empowers informed choices. When shopping, prioritize products that are rich in nutrients while limiting those high in added sugars and unhealthy fats. By doing so, you can efficiently curate a grocery list that aligns with your health objectives.
Establishing a personal eating schedule helps manage hunger and regulate energy levels throughout the day. Aim for three balanced meals interspersed with healthy snacks. This consistency aids in stabilizing blood sugar levels and curtails unhealthy cravings. Simultaneously, integrating regular physical activity is vital. Engaging in brisk walks, jogging, or participating in group fitness classes not only helps burn calories but also enhances overall well-being.
Furthermore, adequate sleep and effective stress management contribute significantly to a healthy diet. Insufficient rest can disrupt hunger hormones, leading to increased cravings for unhealthy options. Techniques such as mindfulness and scheduling downtime are crucial in combatting stress-induced eating. It is also important to recognize common challenges such as time constraints. Planning meals in advance can alleviate the pressure of daily cooking while ensuring that healthy options remain available at all times.
Through these strategies, individuals can cultivate a balanced approach to nutrition, enabling them to enjoy a healthier and more fulfilling life.
The Long-Term Benefits of Healthy Eating

A well-balanced, nutritious diet offers numerous long-term benefits that can positively impact one’s health and well-being. One of the primary advantages of maintaining a healthy eating pattern is the prevention of chronic diseases. Research has consistently shown that a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can significantly reduce the risk of conditions such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and certain types of cancer. For instance, the Mediterranean diet, recognized for its high content of antioxidants and healthy fats, has been linked to lower rates of heart disease and improved metabolic health.
Moreover, healthy eating is crucial for enhancing mental health. Nutritional psychiatry has emerged as a promising field, demonstrating that a diet high in nutrients can improve mood and cognitive function. Consuming omega-3 fatty acids, commonly found in fatty fish and walnuts, has been associated with reduced symptoms of depression and anxiety. Vitamins and minerals, such as B vitamins and magnesium, also play vital roles in brain health, emphasizing the interconnectedness between dietary habits and mental well-being.
Improving longevity is yet another compelling benefit of adopting healthy eating behaviors. Evidence indicates that individuals who prioritize their nutrition are likely to enjoy longer lives free from severe health issues. A study published in the Journal of Nutrition found that adherence to balanced dietary patterns correlates with an increase in life expectancy and a decrease in the risk of premature death.
Investing in a nutritious diet not only boosts physical health but also enhances overall quality of life. Individuals who eat healthily often report higher energy levels, better sleep quality, and improved immune function. In essence, by embracing a balanced diet, one can foster a healthier lifestyle that reaps long-term benefits for both body and mind.
